AI Terms
What is Prompt Engineering? Your Key to AI Success
The same AI that writes brilliant strategies for one person produces mediocre content for another. The difference? How they ask. Prompt engineering has become the most important skill in the AI era, determining whether you get game-changing insights or generic responses from generative AI systems.
From Art to Science
Prompt engineering emerged as a discipline in 2022 as businesses discovered that the way you communicate with AI dramatically affects output quality. What started as trial and error has evolved into a systematic approach.
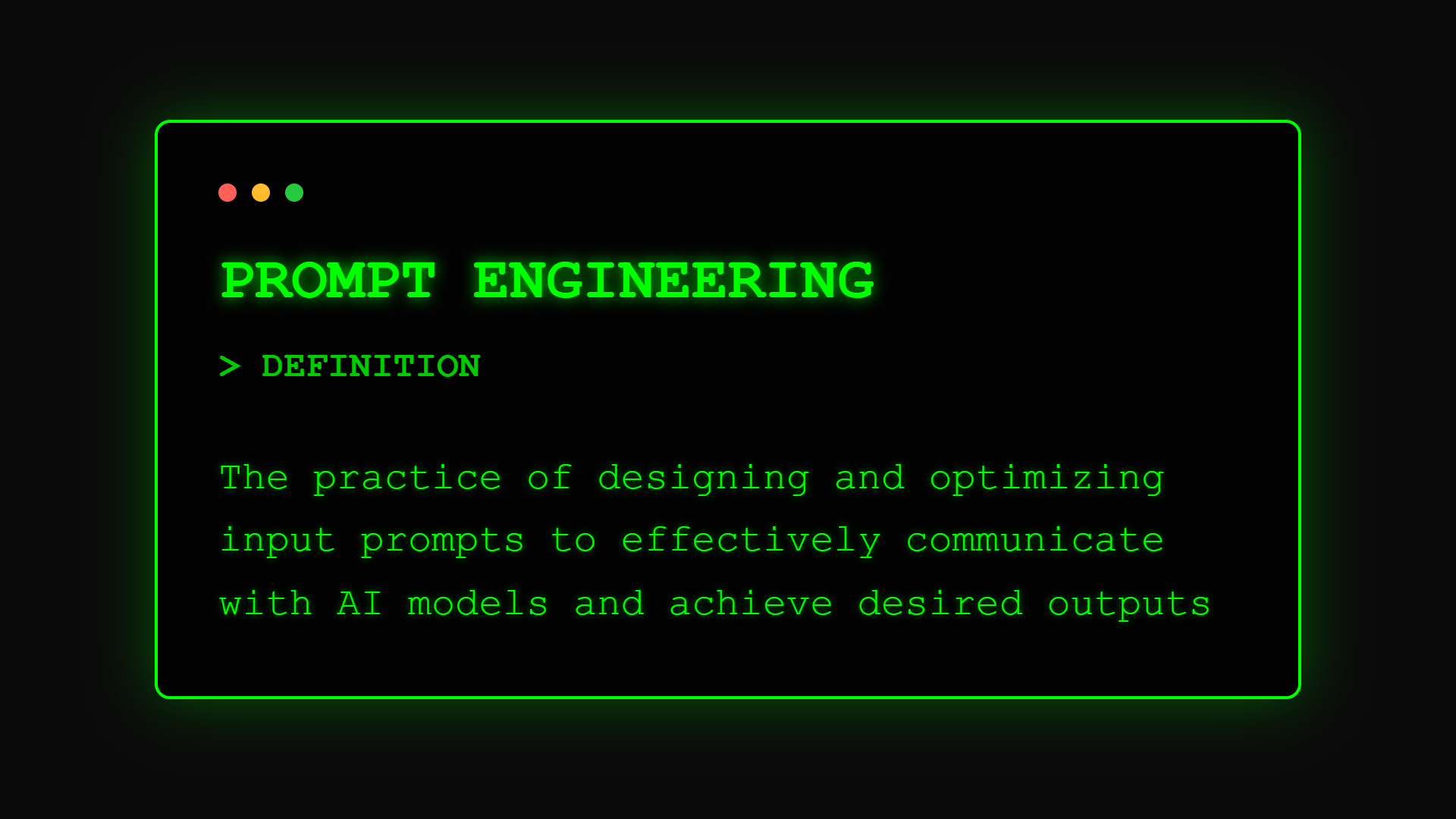
OpenAI defines prompt engineering as "the practice of designing and refining inputs to AI language models to elicit desired outputs, encompassing both the content and structure of instructions to optimize model performance." Understanding how natural language processing works helps you craft more effective prompts.
The field exploded when users realized that GPT-3 could perform vastly different with slight prompt modifications, turning AI interaction from a lottery into a predictable skill.
Making Sense for Business Leaders
For business leaders, prompt engineering means knowing how to communicate with AI systems to get accurate, relevant, and valuable outputs—transforming AI from a unpredictable tool into a reliable business asset.
Think of it as the difference between asking a new employee "do something with the data" versus providing clear, structured instructions with context, examples, and success criteria. The same AI model can be a genius or seem inadequate based solely on how you prompt it.
In practical terms, mastering prompt engineering means getting AI to write better reports, provide more accurate analysis, generate more creative solutions, and deliver more consistent results.
Key Elements of Effective Prompts
Prompt engineering consists of these essential elements:
• Context Setting: Providing background information and defining the AI's role, like "You are a financial analyst reviewing quarterly results for a SaaS company"
• Clear Instructions: Specific, unambiguous directions about what you want, avoiding vague requests like "analyze this" in favor of "identify the top 3 revenue growth drivers"
• Output Format: Defining how you want the response structured, such as "Provide a bullet-point summary followed by detailed analysis"
• Examples: Showing the AI what good output looks like through one or few-shot learning examples
• Constraints: Setting boundaries like word count, tone, or specific requirements that guide the AI's response
The Prompt Engineering Process
Effective prompt engineering follows these steps:
Define Your Objective: Start with crystal clear understanding of what you need. Not "help with marketing" but "create 5 email subject lines for B2B software launch"
Structure Your Prompt: Build prompts systematically: Role → Context → Task → Format → Constraints. Each element guides the AI toward your desired output
Iterate and Refine: Test prompts, analyze outputs, adjust based on results. Small changes like adding "think step-by-step" can dramatically improve reasoning tasks
This iterative process transforms vague AI interactions into predictable, high-quality outputs.
Prompt Engineering Techniques
Prompt engineering employs several key techniques:
Type 1: Zero-Shot Prompting Best for: Simple, straightforward tasks Key feature: Direct instructions without examples Example: "Summarize this article in 3 bullet points"
Type 2: Few-Shot Prompting Best for: Complex or nuanced tasks Key feature: Providing examples of desired output Example: Showing 2-3 examples before requesting similar output
Type 3: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Best for: Reasoning and analysis tasks Key feature: Asking AI to explain its thinking Example: "Analyze this step-by-step and show your reasoning"
Type 4: Role-Based Prompting Best for: Specialized expertise needed Key feature: Assigning AI a specific persona Example: "As an experienced CFO, review this financial plan"
Prompt Engineering in Action
Here's how businesses actually use prompt engineering:
Marketing Example: Jasper.ai users who complete prompt engineering training see 3x improvement in content quality scores and 60% reduction in editing time by using structured prompts with clear brand voice instructions.
Data Analysis Example: McKinsey consultants use carefully engineered prompts to analyze complex datasets, reducing analysis time from days to hours while maintaining accuracy standards.
Customer Service Example: Intercom's AI agents improved resolution rates by 40% after implementing prompt engineering frameworks that include context, tone guidelines, and escalation criteria.
Your Path to Prompt Mastery
Ready to unlock AI's full potential?
- Understand the models with Large Language Models
- Explore advanced techniques in Chain-of-Thought
- Learn to combine AI with data via Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Learn More
Expand your understanding of related AI concepts:
- Tokenization - How AI breaks down and processes your prompts
- Fine-tuning - Customize AI models for specific use cases
- AI Hallucination - Understanding and preventing AI errors
- Conversational AI - Building effective AI dialogue systems
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions about Prompt Engineering
Part of the AI Terms Collection. Last updated: 2026-01-10